In many developed markets, people often invest in a variety of investment products—including investment funds—rather than keeping all their money in one place.

In Georgia, as the financial markets develops, more people are starting to invest their savings in securities and investment funds. However, the majority of savings - 71% - are still held in bank deposits.
In developed European countries, the picture is the opposite: 69% of household savings are placed in funds, securities, and pension/insurance assets.
Looking at Central and Eastern European countries, where banks also play a dominant role, investments in funds are lower than the European average, but still around 30% higher than in Georgia.
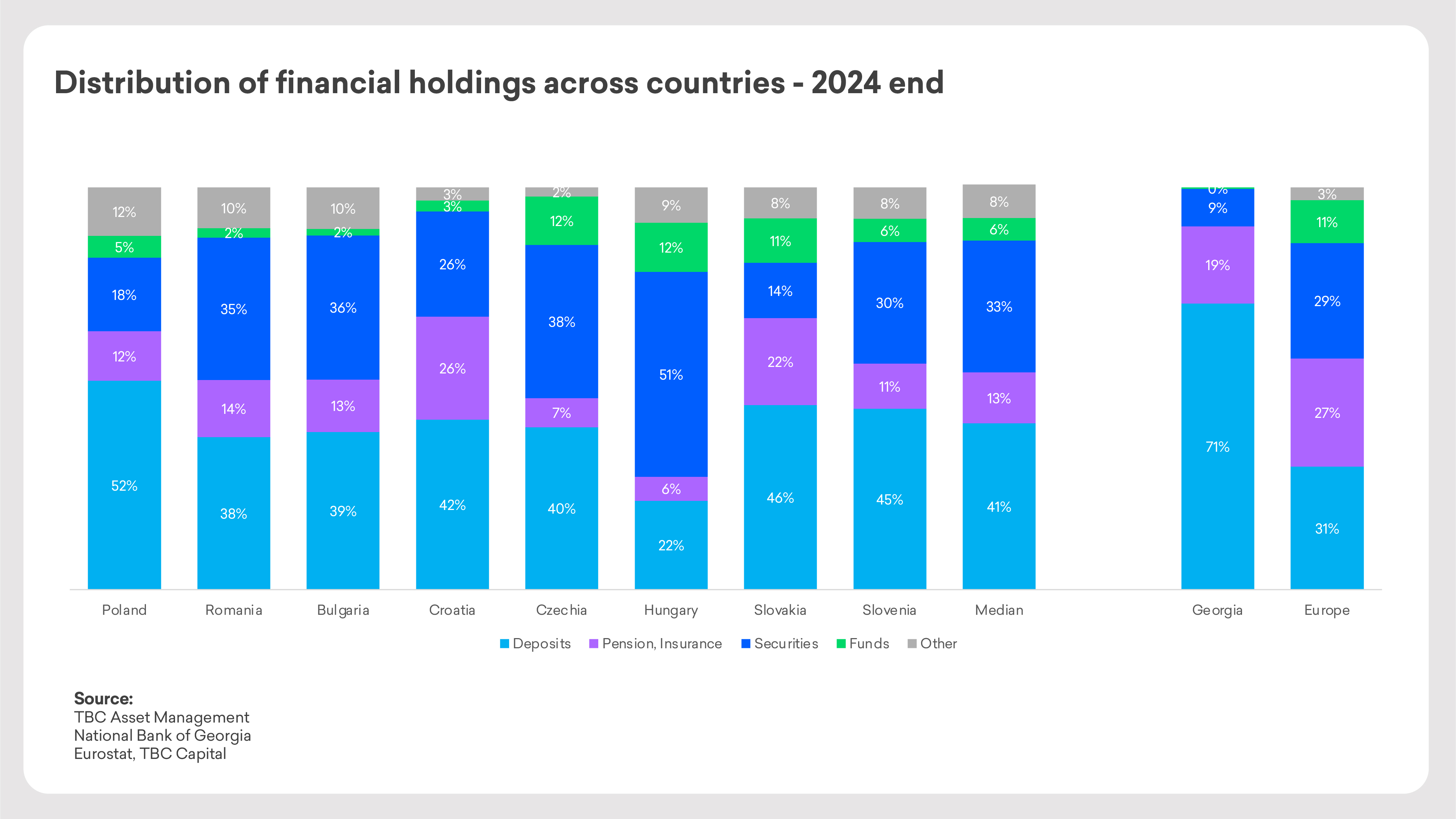
Interestingly, the types of investment funds vary across countries, largely mirroring the trends of their respective capital markets. Georgia follows a similar pattern: the dominant investment strategy today is credit funds, followed by fixed-income and other fund types.
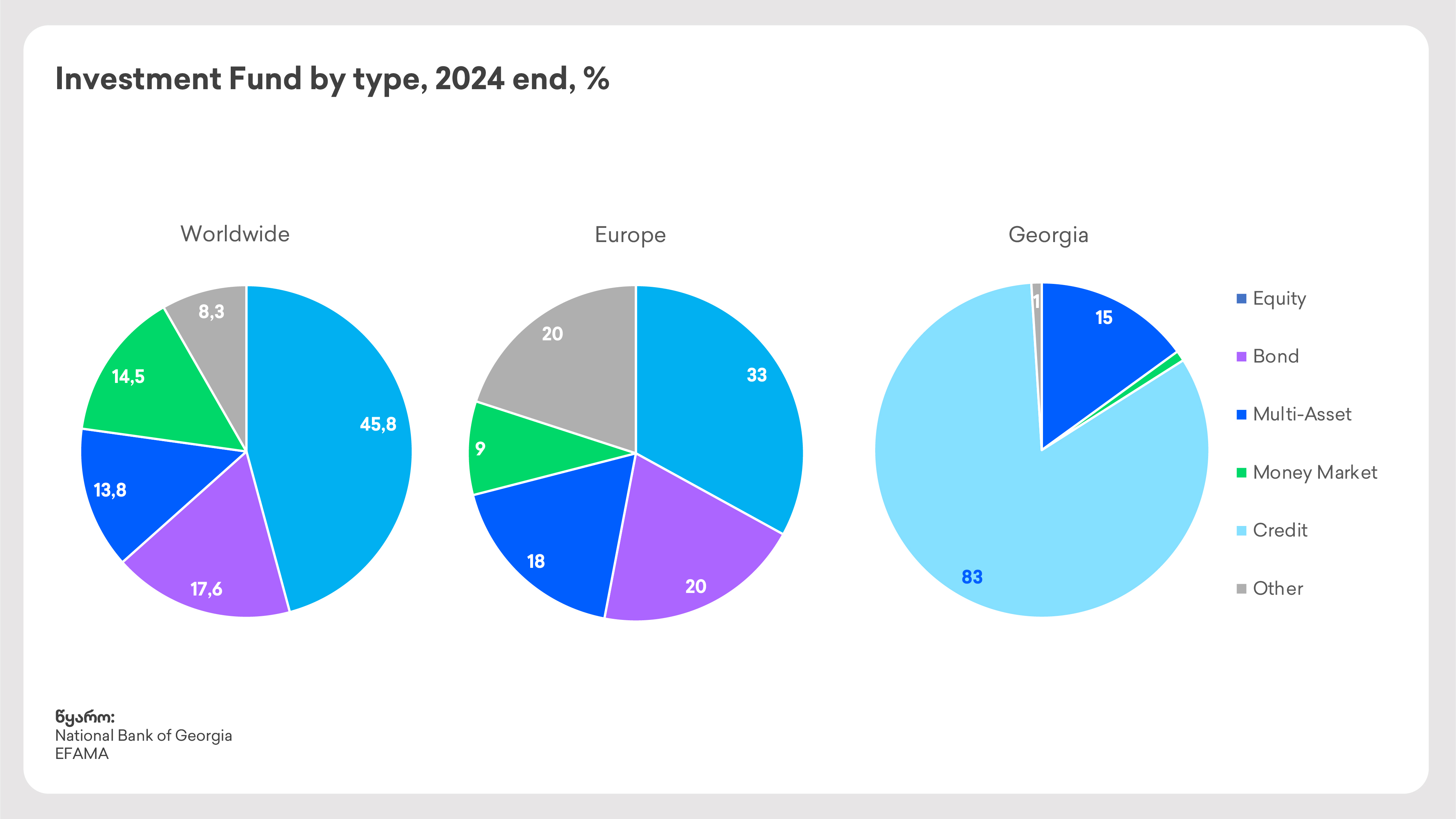
As the market continues to mature, we can expect to see new and more diverse fund options emerging in Georgia, creating fresh opportunities for investors.
WHAT IS AN INVESTMENT FUND?
An investment fund is a collective investment scheme that pools capital from multiple investors and allocates it according to a defined investment policy. The primary goal of the fund is to generate returns for its investors while effectively managing risk.
These funds are managed by professional asset managers or investment companies, who strategically distribute the capital across various financial instruments. Depending on the fund’s objectives, its strategy may focus on:
Capital Growth – Increasing the value of invested assets over time
Income Generation – Providing regular payouts to investors
Risk Reduction – Diversifying investments to minimize exposure
Liquidity Management – Ensuring easy access to funds when needed
By pooling resources, individual investors gain access to a broader range of assets and expert management—advantages that would be difficult to achieve independently.
WHAT TYPES OF INVESTMENT FUNDS EXIST?
Funds typically invest across major asset classes - equities, fixed income, alternative assets, and cash equivalents.
Equities (stocks) provide ownership in companies with higher growth potential and risk, whereas fixed-income instruments (bonds and other debt instruments) offer more stable income streams. Alternative investments encompass assets like real estate, commodities, private equity, or derivatives, which can add diversification benefits. Meanwhile, cash and money market instruments provide short-term, highly liquid holdings for safety or liquidity needs.
A fund’s asset mix will depend on its specific objectives - for example, a growth-oriented fund might hold mostly equities, while an income-oriented fund would likely emphasize bonds and other fixed-income instruments.
WHY INVEST THROUGH A FUND?
Investment funds offer a range of advantages that make them an attractive option for investors:
Access to Unique Asset Assets - Gain exposure to markets and asset classes that are typically difficult for individual investors to access.
Diversification of Risk - Funds spread investments across multiple securities and sectors, reducing the impact of any single asset’s underperformance.
Professional Management - Experienced fund managers leverage in-depth research, advanced analytics, and risk management tools to optimize returns.
Active Oversight and Reinvestment - Managers continuously monitor the portfolio and handle reinvestment decisions, ensuring alignment with the fund’s strategy.
Enhanced Liquidity and Flexibility - Investing through a fund often offers more liquidity and adaptability compared to holding individual securities directly.
Economies of Scale - Pooled resources lower costs related to administration, reporting, and research, making investing more cost-efficient.
Regulatory Oversight and Transparency - Funds operate under strict regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance, accountability, and clear reporting standards.
